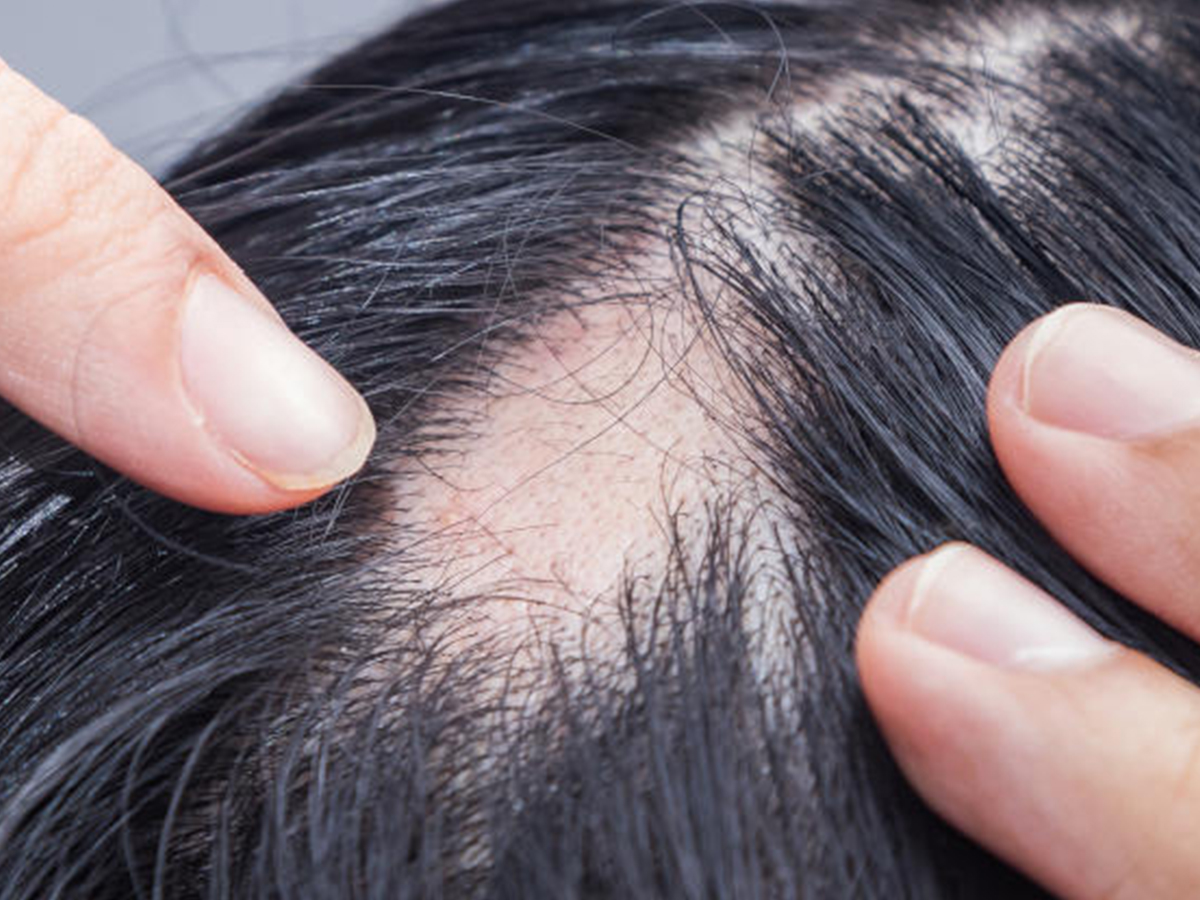
Alopecia is a broad term used to describe various types of hair loss that occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss in patches or across the entire scalp. While the exact cause of alopecia is not fully understood, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and autoimmune factors.
There are several types of alopecia, each with its own distinct characteristics and patterns of hair loss. The most common form is alopecia areata, which typically presents as smooth, round patches of hair loss on the scalp or other hair-bearing areas of the body. In some cases, alopecia areata may progress to more extensive forms of hair loss, such as alopecia totalis (loss of all scalp hair) or alopecia universalis (loss of all body hair).
While the exact cause of alopecia areata remains unclear, it is thought to involve a complex interplay between genetic predisposition and autoimmune dysfunction. In individuals with alopecia areata, the immune system mistakenly targets hair follicles as foreign invaders, leading to inflammation and subsequent hair loss. Triggers such as stress, illness, hormonal changes, or environmental factors may exacerbate the condition and precipitate flare-ups.
Treatment options for alopecia areata vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. For mild cases involving small, localized patches of hair loss, topical treatments such as corticosteroids or minoxidil may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and stimulate hair regrowth. In more severe or widespread cases, systemic treatments such as oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologic agents may be recommended to modulate the immune response and suppress autoimmune activity.
In addition to conventional medical treatments, individuals with alopecia areata may benefit from supportive therapies and lifestyle modifications aimed at promoting overall health and well-being. Stress management techniques, regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can help reduce stress levels and support immune function, potentially minimizing the risk of flare-ups and improving treatment outcomes.
For individuals with more extensive or refractory forms of alopecia, hair transplantation may be considered as a permanent solution to restore hair density and coverage. Follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE) are the two primary techniques used to transplant healthy hair follicles from donor sites to recipient areas of the scalp, resulting in natural-looking hair restoration.
In conclusion, alopecia is a complex and challenging condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management. By consulting with a qualified dermatologist or hair restoration specialist, individuals with alopecia can explore various treatment options and develop a personalized plan to address their specific needs and goals. With the right combination of medical therapies, supportive care, and lifestyle modifications, individuals with alopecia can achieve improved hair growth and regain their confidence and quality of life.
