Acne is one of the most common skin conditions affecting people of all ages, especially teenagers and young adults. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. While many people consider acne a minor cosmetic issue, severe cases can cause scarring and emotional distress. Understanding the different types of acne, their causes, and available treatments is essential for effective management.
This blog will explore the various types of acne, their symptoms, potential causes, and the best treatment options to help you achieve clearer skin.
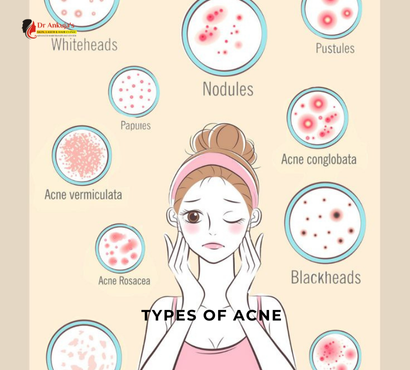
Types of Acne
Acne can be classified into two main categories: non-inflammatory acne and inflammatory acne. Each type has distinct characteristics and requires specific treatments.
1. Non-Inflammatory Acne
Non-inflammatory acne includes blackheads and whiteheads, which do not cause redness or swelling.
A. Blackheads (Open Comedones)
- Symptoms: Small, dark spots on the skin that appear black due to oxidation of oil and debris.
- Causes: Excess oil production, clogged pores, improper skincare routine.
- Treatment:
- Use of salicylic acid cleansers to unclog pores.
- Regular exfoliation to remove dead skin cells.
- Avoiding excessive use of oily skincare products.
B. Whiteheads (Closed Comedones)
- Symptoms: Small, white or flesh-colored bumps that form when a clogged pore remains closed.
- Causes: Oil buildup, hormonal fluctuations, poor skincare habits.
- Treatment:
- Topical retinoids like adapalene to promote skin cell turnover.
- Gentle cleansing and proper hydration.
- Avoid squeezing or popping whiteheads to prevent scarring.
2. Inflammatory Acne
Inflammatory acne involves redness, swelling, and discomfort. It can range from mild to severe and often requires medical intervention.
A. Papules
- Symptoms: Small, red, tender bumps on the skin.
- Causes: Bacterial infection, excess oil, dead skin cells.
- Treatment:
- Benzoyl peroxide to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
- Prescription-strength retinoids for severe cases.
- Avoid harsh scrubs that can worsen inflammation.
B. Pustules
- Symptoms: Pimples filled with pus, surrounded by red, inflamed skin.
- Causes: Bacterial overgrowth, hormonal changes, poor hygiene.
- Treatment:
- Topical antibiotics like clindamycin to fight bacteria.
- Oral antibiotics for persistent breakouts.
- A balanced diet to reduce inflammatory triggers.
C. Nodules
- Symptoms: Large, hard, painful lumps deep under the skin.
- Causes: Severe clogging of pores, hormonal fluctuations, genetic predisposition.
- Treatment:
- Oral isotretinoin (Accutane) for severe cases.
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce swelling.
- Professional dermatological care.
D. Cystic Acne
- Symptoms: Large, pus-filled cysts that can be painful and lead to scarring.
- Causes: Severe hormonal imbalance, bacterial infection, excess oil production.
- Treatment:
- Oral isotretinoin for long-term relief.
- Hormonal therapy like oral contraceptives for women with hormonal acne.
- Dermatological procedures such as drainage or laser therapy.
Common Causes of Acne
Several factors contribute to acne breakouts. Understanding these triggers can help in preventing and managing acne.
1. Hormonal Changes
- Fluctuations in hormones, especially during puberty, pregnancy, and menstruation, can increase oil production and trigger acne.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common cause of persistent hormonal acne in women.
2. Excess Oil Production
- Overactive sebaceous (oil) glands can clog pores and lead to acne formation.
3. Bacterial Growth
- The presence of Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria on the skin contributes to inflammation and pus formation.
4. Diet and Lifestyle
- High-glycemic foods (e.g., sugar, processed carbohydrates) may worsen acne.
- Dairy products have been linked to breakouts in some individuals.
- Stress increases cortisol levels, which can lead to acne flare-ups.
5. Skincare and Hygiene
- Using comedogenic (pore-clogging) products can aggravate acne.
- Improper cleansing or over-washing the face can disrupt the skin’s natural balance.
Effective Treatments for Acne
There are multiple treatment options available depending on the severity and type of acne.
1. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
- Salicylic acid: Helps unclog pores and prevent breakouts.
- Benzoyl peroxide: Kills acne-causing bacteria and reduces inflammation.
- Retinoids (Adapalene, Retinol): Promote skin cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.
2. Prescription Medications
- Oral antibiotics (Doxycycline, Minocycline): Used for moderate to severe acne to control bacterial infection.
- Isotretinoin (Accutane): A powerful medication for severe cystic acne that shrinks oil glands and prevents new acne from forming.
- Hormonal treatments (Oral contraceptives, Spironolactone): Used for hormonal acne in women.
3. Dermatological Procedures
- Chemical Peels: Exfoliate the skin and improve acne scars.
- Laser Therapy: Reduces acne-causing bacteria and inflammation.
- Microneedling: Stimulates collagen production to heal acne scars.
Tips to Prevent Acne
✔ Follow a consistent skincare routine with gentle cleansing.
✔ Use non-comedogenic (oil-free) products to avoid clogging pores.
✔ Stay hydrated to keep the skin healthy.
✔ Manage stress with relaxation techniques like yoga and meditation.
✔ Avoid touching your face to prevent bacterial transfer.
✔ Eat a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can be frustrating, understanding the different types of acne, their causes, and effective treatment options can help in managing breakouts and achieving healthier skin. Whether you have mild or severe acne, early intervention and the right skincare routine can make a significant difference.If you’re struggling with persistent acne, consider consulting a dermatologist for a personalized treatment plan. Clear skin is possible with the right approach!
FAQ
1. Can stress cause acne?
Yes, stress increases cortisol levels, which can lead to excess oil production and inflammation, causing acne flare-ups.
2. How long does it take for acne treatments to work?
Most acne treatments take 4-6 weeks to show noticeable results, but severe cases may require 3-6 months for significant improvement.
3. Can diet affect acne?
Yes, high-glycemic foods, dairy products, and excessive sugar intake can worsen acne in some individuals. A balanced diet can help manage breakouts.